Python
内置数据类型
内置类型:
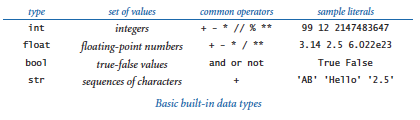
类型转换:
- str(x)
- int(x)
- float(x)
- round(x)
内置数据结构
- List(as Stacks Queues),[],可变序列
- Tuples,(),不可变序列
- Sets,{},无序,唯一
- Dicts,{},键值对,键唯一
List生成式
直接生成:
>>> list(range(1, 11))
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
生成后再处理:
>>> [x * x for x in range(1, 11)]
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]
生成后再条件处理:
>>> [x if x % 2 == 0 else -x for x in range(1, 11)]
[-1, 2, -3, 4, -5, 6, -7, 8, -9, 10]
生成后先过滤再处理:
>>> [x * x for x in range(1, 11) if x % 2 == 0]
[4, 16, 36, 64, 100]
双循环:
>>> [m + n for m in 'ABC' for n in 'XYZ']
['AX', 'AY', 'AZ', 'BX', 'BY', 'BZ', 'CX', 'CY', 'CZ']
内置高级数据结构
collections
- namedtuple,自定义的tuple对象
def test_namedtuple():
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
p = Point(1, 2)
print(p)
- deque,高效双向列表,适合用于队列和栈
def test_deque():
q = deque(['a', 'b', 'c'])
q.append('x')
q.appendleft('y')
print(q)
- defaultdict,带默认值的dict
def test_defaultdict():
dd = defaultdict(lambda: 'N/A')
dd['key1'] = 'abc'
print(dd['key1'])
print(dd['key2'])
- OrderedDict,插入有序的dict
def test_ordereddict():
od = OrderedDict([('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 3)])
print(od)
- ChainMap,逻辑组合的dict
def test_chainmap():
d1 = {'a': 1}
d2 = {'b': 2}
cd = ChainMap(d1, d2)
print(cd)
- Counter,计数器
def test_counter():
c = Counter()
for ch in 'helloword':
c[ch] = c[ch] + 1
print(c)
heapq
- heapq,优先级队列
def test_heapq():
h = []
heapq.heappush(h, 5)
heapq.heappush(h, 7)
heapq.heappush(h, 1)
heapq.heappush(h, 3)
print(h)
print(heapq.nlargest(2, h))
print(heapq.nsmallest(2, h))
循环控制
- if
- while
- for
其他:
- range,范围
- break,中断
- continue,跳过
- else,后置
- pass,占位
遍历
for ... in ...
- items(),键值对遍历
- enumerate(),带索引遍历
- zip(),并行遍历
- reversed(),逆序遍历
- sorted(),有序遍历
函数式编程
map
map()函数接收两个参数,一个是函数,一个是Iterable,map将传入的函数依次作用到序列的每个元素,并把结果作为新的Iterator返回
def test_map():
def f(x):
return x * x
r = map(f, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
print(list(r))
reduce
reduce()把一个函数作用在一个序列[x1, x2, x3, …]上,这个函数必须接收两个参数,reduce把结果继续和序列的下一个元素做累积计算
def test_reduce():
def f(x, y):
return x + y
r = reduce(f, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
print(r)
filter
filter()函数接收两个参数,一个是函数,一个是Iterable,filter传入的函数依次作用于每个元素,然后根据返回值是True还是False决定保留还是丢弃该元素,并把结果作为新的Iterator返回
def test_filter():
def f(n):
return n % 2 == 1
r = filter(f, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
print(list(r))
sorted
sorted()函数可以对list进行排序,还可以接收一个key函数来实现自定义的排序,key指定的函数将作用于list的每一个元素上,并根据key函数返回的结果进行排序
def test_sorted():
print(sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21], key=abs))
print(sorted([36, 5, -12, 9, -21], key=abs, reverse=True))
lambda
匿名函数,冒号前面的x表示函数参数
lambda x: x * x实际上就是
def f(x):
return x * x
def test_lambda():
r = map(lambda x: x * x, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
print(list(r))